OpenAI Whisper: The Revolutionary Speech Recognition System That's Transforming Audio Processing with 92k+ GitHub Stars
Master OpenAI Whisper's revolutionary speech recognition capabilities. Learn installation, model selection, command-line usage, Python integration, and real-world applications with practical code examples.
OpenAI Whisper: The Revolutionary Speech Recognition System That's Transforming Audio Processing with 92k+ GitHub Stars
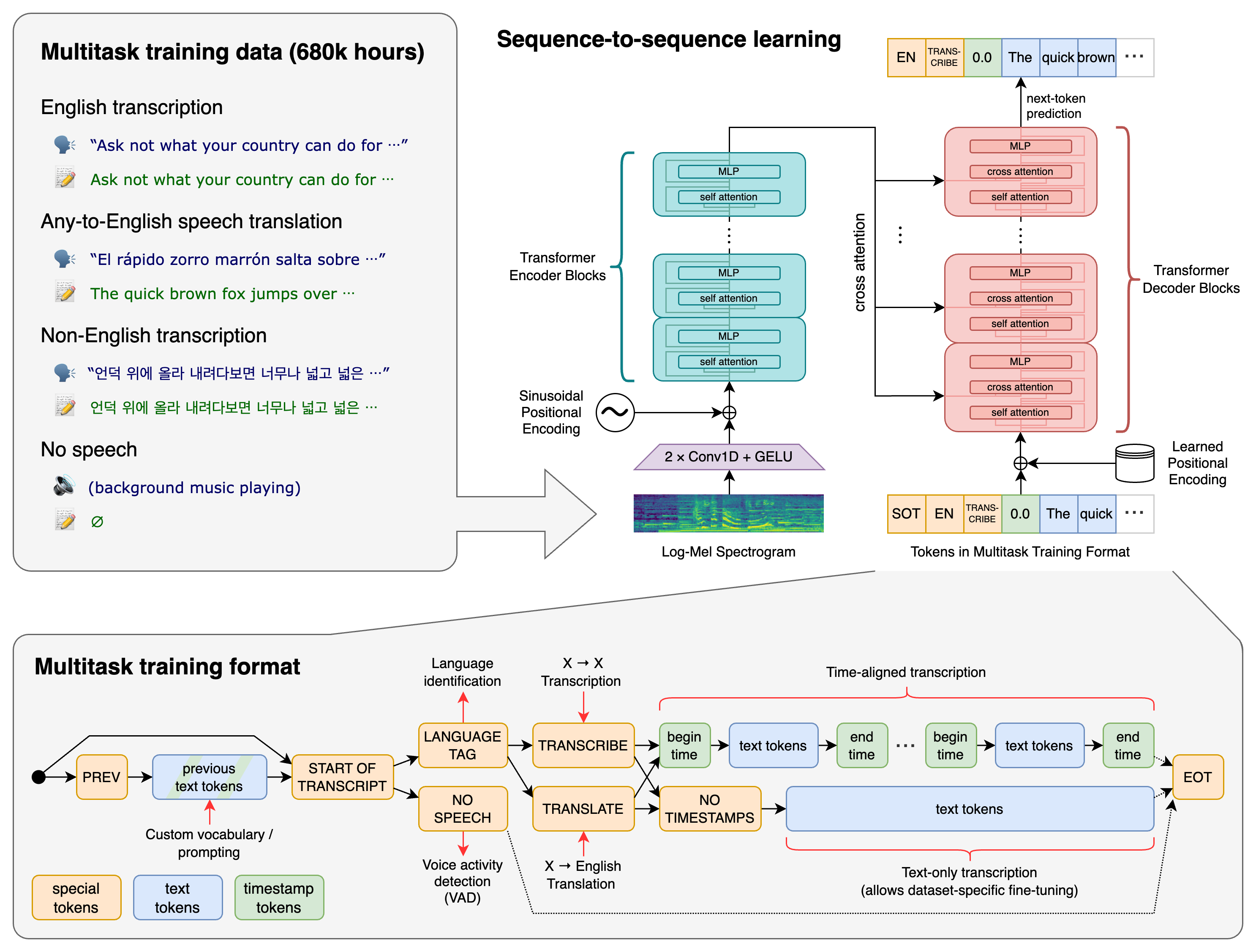
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, few tools have made as significant an impact on speech recognition as OpenAI's Whisper. With over 92,900 GitHub stars and a robust architecture trained on diverse audio data, Whisper has become the go-to solution for developers, researchers, and businesses looking to implement state-of-the-art speech recognition capabilities.

What Makes Whisper Revolutionary?
Whisper isn't just another speech recognition model—it's a general-purpose, multitasking system that can perform:
- Multilingual speech recognition across 99+ languages
- Speech translation to English from any supported language
- Language identification for automatic language detection
- Voice activity detection to identify speech segments
What sets Whisper apart is its transformer-based sequence-to-sequence architecture that handles all these tasks within a single model, eliminating the need for complex multi-stage pipelines.
Installation and Setup
Getting started with Whisper is remarkably straightforward. Here's how to set it up on your system:
Basic Installation
# Install the latest release
pip install -U openai-whisper
# Or install from the latest GitHub commit
pip install git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.gitSystem Dependencies
Whisper requires FFmpeg for audio processing. Install it based on your operating system:
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update && sudo apt install ffmpeg
# macOS (using Homebrew)
brew install ffmpeg
# Windows (using Chocolatey)
choco install ffmpeg
# Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S ffmpegAdditional Requirements
If you encounter installation issues, you may need Rust and setuptools-rust:
# Install setuptools-rust if needed
pip install setuptools-rust
# Configure PATH for Rust (if required)
export PATH="$HOME/.cargo/bin:$PATH"Understanding Whisper's Model Lineup
Whisper offers six different model sizes, each optimized for different use cases and hardware constraints:
| Size | Parameters | English-only | Multilingual | VRAM Required | Relative Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tiny | 39M | tiny.en | tiny | ~1 GB | ~10x |
| base | 74M | base.en | base | ~1 GB | ~7x |
| small | 244M | small.en | small | ~2 GB | ~4x |
| medium | 769M | medium.en | medium | ~5 GB | ~2x |
| large | 1550M | N/A | large | ~10 GB | 1x |
| turbo | 809M | N/A | turbo | ~6 GB | ~8x |
Pro Tip: The turbo model offers the best balance of speed and accuracy for most applications, but remember it's not trained for translation tasks. For translation, use the medium or large models.
Command-Line Usage: Quick Start Guide
Whisper's command-line interface makes it incredibly easy to transcribe audio files:
Basic Transcription
# Transcribe multiple audio files using the turbo model
whisper audio.flac audio.mp3 audio.wav --model turbo
# Specify language for better accuracy
whisper japanese.wav --language Japanese
# Translate non-English speech to English
whisper japanese.wav --model medium --language Japanese --task translateAdvanced Options
# View all available options
whisper --help
# Output to specific formats
whisper audio.mp3 --output_format txt
whisper audio.mp3 --output_format srt # For subtitles
whisper audio.mp3 --output_format vtt # WebVTT formatPython Integration: Building Powerful Applications
Whisper's Python API opens up endless possibilities for integration into your applications:
Basic Python Usage
import whisper
# Load the model (downloads automatically on first use)
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
# Transcribe audio
result = model.transcribe("audio.mp3")
print(result["text"])
# Access additional information
print(f"Language: {result['language']}")
print(f"Segments: {len(result['segments'])}")Advanced Processing with Lower-Level API
import whisper
import numpy as np
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
# Load and preprocess audio
audio = whisper.load_audio("audio.mp3")
audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio) # Fit to 30 seconds
# Create mel spectrogram
mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio, n_mels=model.dims.n_mels).to(model.device)
# Detect language
_, probs = model.detect_language(mel)
detected_language = max(probs, key=probs.get)
print(f"Detected language: {detected_language} (confidence: {probs[detected_language]:.2f})")
# Decode with custom options
options = whisper.DecodingOptions(
language=detected_language,
task="transcribe", # or "translate"
fp16=False # Use fp32 for better accuracy on CPU
)
result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options)
print(result.text)Batch Processing for Multiple Files
import whisper
import os
from pathlib import Path
def batch_transcribe(audio_dir, output_dir, model_name="turbo"):
"""Transcribe all audio files in a directory"""
model = whisper.load_model(model_name)
audio_extensions = ('.mp3', '.wav', '.flac', '.m4a', '.ogg')
audio_files = [f for f in Path(audio_dir).iterdir()
if f.suffix.lower() in audio_extensions]
results = []
for audio_file in audio_files:
print(f"Processing: {audio_file.name}")
try:
result = model.transcribe(str(audio_file))
# Save transcription
output_file = Path(output_dir) / f"{audio_file.stem}.txt"
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(result["text"])
results.append({
'file': audio_file.name,
'language': result['language'],
'duration': len(result['segments']),
'text': result['text'][:100] + '...' # Preview
})
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {audio_file.name}: {e}")
results.append({
'file': audio_file.name,
'error': str(e)
})
return results
# Usage
results = batch_transcribe("./audio_files", "./transcriptions")
for result in results:
print(result)Real-World Applications and Use Cases
1. Meeting Transcription System
import whisper
from datetime import datetime
import json
class MeetingTranscriber:
def __init__(self, model_name="turbo"):
self.model = whisper.load_model(model_name)
def transcribe_meeting(self, audio_file, participants=None):
"""Transcribe a meeting with timestamps and speaker detection"""
result = self.model.transcribe(
audio_file,
word_timestamps=True,
verbose=True
)
meeting_data = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'language': result['language'],
'participants': participants or [],
'full_text': result['text'],
'segments': []
}
for segment in result['segments']:
meeting_data['segments'].append({
'start': segment['start'],
'end': segment['end'],
'text': segment['text'],
'words': segment.get('words', [])
})
return meeting_data
def save_transcript(self, meeting_data, output_file):
"""Save transcript in multiple formats"""
# JSON format
with open(f"{output_file}.json", 'w') as f:
json.dump(meeting_data, f, indent=2)
# Human-readable format
with open(f"{output_file}.txt", 'w') as f:
f.write(f"Meeting Transcript - {meeting_data['timestamp']}\n")
f.write(f"Language: {meeting_data['language']}\n\n")
for segment in meeting_data['segments']:
timestamp = f"[{segment['start']:.1f}s - {segment['end']:.1f}s]"
f.write(f"{timestamp} {segment['text']}\n")
# Usage
transcriber = MeetingTranscriber()
meeting = transcriber.transcribe_meeting(
"team_meeting.mp3",
participants=["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
)
transcriber.save_transcript(meeting, "meeting_2026_01_08")2. Multilingual Content Processing
import whisper
from collections import Counter
class MultilingualProcessor:
def __init__(self):
self.model = whisper.load_model("large") # Best for translation
def process_multilingual_content(self, audio_files):
"""Process multiple audio files in different languages"""
results = []
language_stats = Counter()
for audio_file in audio_files:
print(f"Processing: {audio_file}")
# First, detect language
audio = whisper.load_audio(audio_file)
audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio)
mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio, n_mels=self.model.dims.n_mels).to(self.model.device)
_, probs = self.model.detect_language(mel)
detected_lang = max(probs, key=probs.get)
confidence = probs[detected_lang]
# Transcribe in original language
transcription = self.model.transcribe(
audio_file,
language=detected_lang,
task="transcribe"
)
# Translate to English if not English
translation = None
if detected_lang != 'en':
translation = self.model.transcribe(
audio_file,
language=detected_lang,
task="translate"
)
result = {
'file': audio_file,
'detected_language': detected_lang,
'confidence': confidence,
'original_text': transcription['text'],
'english_translation': translation['text'] if translation else None
}
results.append(result)
language_stats[detected_lang] += 1
return results, language_stats
# Usage
processor = MultilingualProcessor()
files = ["spanish_audio.mp3", "french_audio.wav", "english_audio.flac"]
results, stats = processor.process_multilingual_content(files)
print(f"Language distribution: {dict(stats)}")
for result in results:
print(f"File: {result['file']}")
print(f"Language: {result['detected_language']} ({result['confidence']:.2f})")
print(f"Original: {result['original_text'][:100]}...")
if result['english_translation']:
print(f"Translation: {result['english_translation'][:100]}...")
print("-" * 50)Performance Optimization Tips
1. Model Selection Strategy
- For real-time applications: Use
tinyorbasemodels - For high accuracy: Use
largeorturbomodels - For English-only content: Use
.envariants for better performance - For translation tasks: Avoid
turbo, usemediumorlarge
2. Hardware Optimization
import whisper
import torch
# Check for GPU availability
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
# Load model with specific device
model = whisper.load_model("turbo", device=device)
# For CPU optimization
if device == "cpu":
# Use fp32 for better accuracy on CPU
options = whisper.DecodingOptions(fp16=False)
else:
# Use fp16 for faster GPU processing
options = whisper.DecodingOptions(fp16=True)3. Memory Management for Large Files
def transcribe_large_file(audio_file, model_name="turbo", chunk_length=30):
"""Transcribe large audio files in chunks"""
import librosa
model = whisper.load_model(model_name)
# Load audio
audio, sr = librosa.load(audio_file, sr=16000)
# Calculate chunk size in samples
chunk_samples = chunk_length * sr
transcripts = []
for i in range(0, len(audio), chunk_samples):
chunk = audio[i:i + chunk_samples]
# Pad if necessary
if len(chunk) < chunk_samples:
chunk = np.pad(chunk, (0, chunk_samples - len(chunk)))
# Transcribe chunk
result = model.transcribe(chunk)
transcripts.append(result['text'])
print(f"Processed chunk {i//chunk_samples + 1}")
return ' '.join(transcripts)
# Usage for large files
long_transcript = transcribe_large_file("long_podcast.mp3")Integration with Popular Frameworks
FastAPI Web Service
from fastapi import FastAPI, File, UploadFile, HTTPException
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
import whisper
import tempfile
import os
app = FastAPI(title="Whisper Transcription API")
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
@app.post("/transcribe")
async def transcribe_audio(file: UploadFile = File(...), language: str = None):
"""Transcribe uploaded audio file"""
if not file.content_type.startswith('audio/'):
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="File must be audio format")
try:
# Save uploaded file temporarily
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix='.wav') as tmp_file:
content = await file.read()
tmp_file.write(content)
tmp_file_path = tmp_file.name
# Transcribe
options = {}
if language:
options['language'] = language
result = model.transcribe(tmp_file_path, **options)
# Clean up
os.unlink(tmp_file_path)
return JSONResponse({
"text": result["text"],
"language": result["language"],
"segments": len(result["segments"])
})
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
@app.get("/models")
def list_models():
"""List available Whisper models"""
return {
"models": [
{"name": "tiny", "size": "39M", "speed": "10x"},
{"name": "base", "size": "74M", "speed": "7x"},
{"name": "small", "size": "244M", "speed": "4x"},
{"name": "medium", "size": "769M", "speed": "2x"},
{"name": "large", "size": "1550M", "speed": "1x"},
{"name": "turbo", "size": "809M", "speed": "8x"}
]
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. Installation Problems
# If you get "No module named 'setuptools_rust'"
pip install setuptools-rust
# If tiktoken installation fails
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install tiktoken
# For M1/M2 Macs with PyTorch issues
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu2. Memory Issues
# Reduce memory usage
import gc
import torch
# Clear GPU cache
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# Force garbage collection
gc.collect()
# Use smaller model for memory-constrained environments
model = whisper.load_model("tiny") # Instead of "large"3. Audio Format Issues
import subprocess
def convert_audio_format(input_file, output_file):
"""Convert audio to compatible format using FFmpeg"""
cmd = [
'ffmpeg', '-i', input_file,
'-ar', '16000', # Sample rate
'-ac', '1', # Mono
'-c:a', 'pcm_s16le', # PCM 16-bit
output_file
]
subprocess.run(cmd, check=True)
# Usage
convert_audio_format("input.m4a", "output.wav")
result = model.transcribe("output.wav")Best Practices and Production Considerations
1. Error Handling and Logging
import logging
import whisper
from typing import Optional, Dict, Any
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class RobustWhisperTranscriber:
def __init__(self, model_name: str = "turbo"):
try:
self.model = whisper.load_model(model_name)
logger.info(f"Loaded Whisper model: {model_name}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to load model {model_name}: {e}")
raise
def transcribe_with_retry(self, audio_file: str, max_retries: int = 3) -> Optional[Dict[Any, Any]]:
"""Transcribe with retry logic and error handling"""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
logger.info(f"Transcribing {audio_file} (attempt {attempt + 1})")
result = self.model.transcribe(audio_file)
logger.info(f"Successfully transcribed {audio_file}")
return result
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(f"Attempt {attempt + 1} failed for {audio_file}: {e}")
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
logger.error(f"All attempts failed for {audio_file}")
return None
return None2. Performance Monitoring
import time
from contextlib import contextmanager
@contextmanager
def timer(description: str):
"""Context manager for timing operations"""
start = time.time()
yield
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"{description}: {elapsed:.2f} seconds")
# Usage
with timer("Model loading"):
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
with timer("Transcription"):
result = model.transcribe("audio.mp3")Future Developments and Community
The Whisper ecosystem continues to evolve rapidly:
- Model Updates: OpenAI regularly releases improved versions (latest: large-v3-turbo)
- Community Extensions: Third-party tools for real-time transcription, web interfaces, and mobile apps
- Integration Ecosystem: Growing support in popular frameworks like Hugging Face Transformers
- Performance Improvements: Ongoing optimizations for edge devices and cloud deployment
Conclusion
OpenAI Whisper has fundamentally changed the landscape of speech recognition technology. Its combination of accuracy, multilingual support, and ease of use makes it an invaluable tool for developers building audio-processing applications. Whether you're creating meeting transcription systems, multilingual content platforms, or accessibility tools, Whisper provides the robust foundation you need.
The model's open-source nature, comprehensive documentation, and active community ensure that it will continue to be a cornerstone of modern AI applications. As you build your next audio-processing project, Whisper's proven track record and 92,900+ GitHub stars speak to its reliability and effectiveness.
For more expert insights and tutorials on AI and automation, visit us at decisioncrafters.com.