Master OpenAI Whisper: Complete Guide to AI-Powered Speech Recognition
OpenAI Whisper has revolutionized speech recognition with its robust, multilingual capabilities. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about implementing and using Whisper for your AI projects.
Master OpenAI Whisper: Complete Guide to AI-Powered Speech Recognition
OpenAI Whisper has revolutionized speech recognition with its robust, multilingual capabilities. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about implementing and using Whisper for your AI projects.
What is OpenAI Whisper?
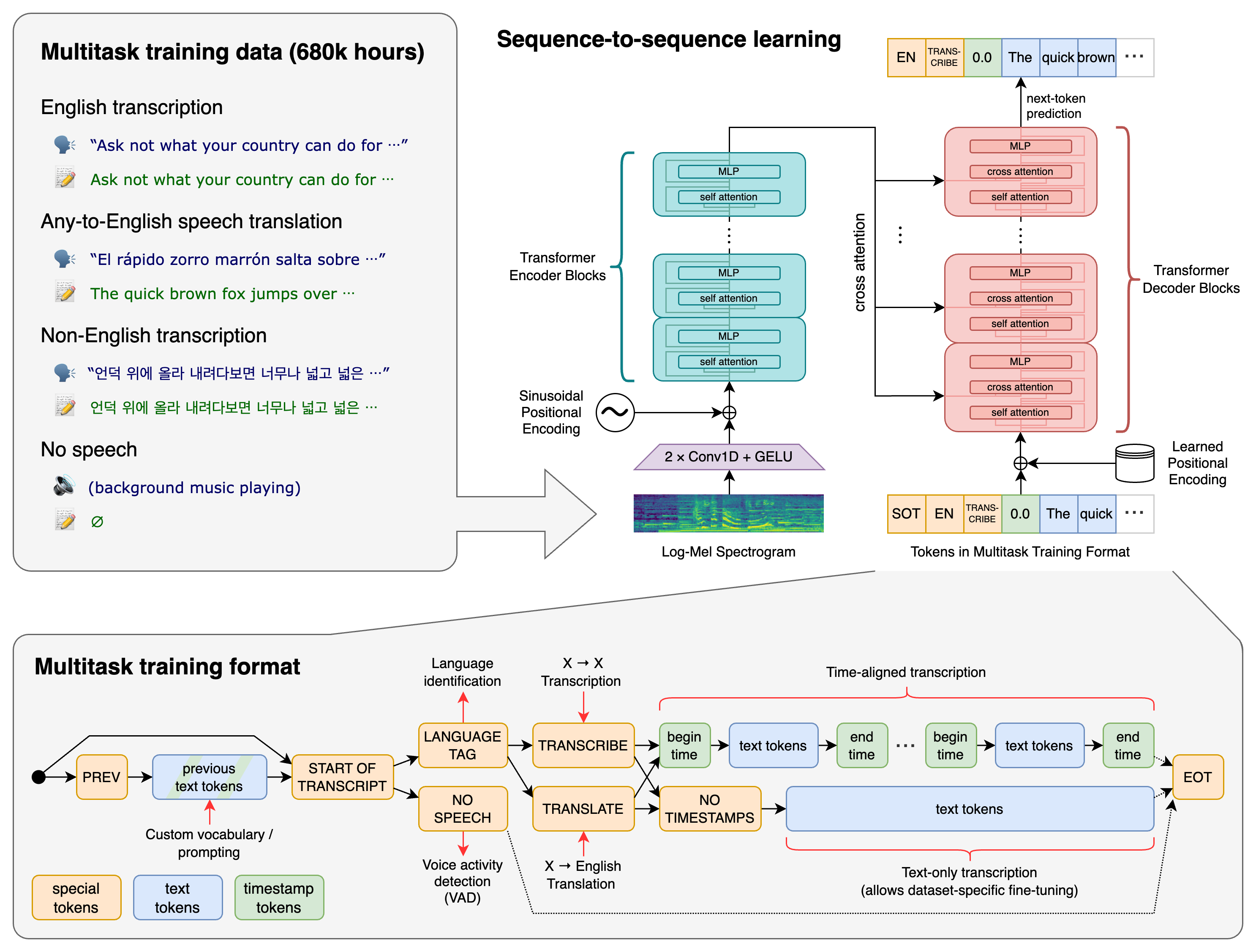
Whisper is a general-purpose speech recognition model developed by OpenAI. It's trained on a massive dataset of diverse audio and can perform multiple tasks:
- Multilingual speech recognition - Transcribe speech in dozens of languages
- Speech translation - Translate non-English speech directly to English
- Language identification - Automatically detect the spoken language
- Voice activity detection - Identify when speech is present

Installation and Setup
Step 1: Install Whisper
The easiest way to install Whisper is via pip:
pip install -U openai-whisperFor the latest development version:
pip install git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.gitStep 2: Install FFmpeg
Whisper requires FFmpeg for audio processing. Install it based on your operating system:
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt update && sudo apt install ffmpeg
# macOS (with Homebrew)
brew install ffmpeg
# Windows (with Chocolatey)
choco install ffmpeg
# Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S ffmpegStep 3: Handle Dependencies
If you encounter installation issues, you may need Rust and setuptools-rust:
pip install setuptools-rustAvailable Models and Performance
Whisper offers six model sizes with different speed and accuracy tradeoffs:
| Size | Parameters | English Model | Multilingual | VRAM | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tiny | 39M | tiny.en | tiny | ~1 GB | ~10x |
| base | 74M | base.en | base | ~1 GB | ~7x |
| small | 244M | small.en | small | ~2 GB | ~4x |
| medium | 769M | medium.en | medium | ~5 GB | ~2x |
| large | 1550M | N/A | large | ~10 GB | 1x |
| turbo | 809M | N/A | turbo | ~6 GB | ~8x |
Command-Line Usage
Basic Transcription
Transcribe audio files using the turbo model (default):
whisper audio.flac audio.mp3 audio.wav --model turboLanguage-Specific Transcription
For non-English audio, specify the language:
whisper japanese.wav --language JapaneseTranslation to English
Translate non-English speech directly to English:
whisper japanese.wav --model medium --language Japanese --task translateImportant: The turbo model doesn't support translation. Use medium or large models for translation tasks.
Python Integration
Basic Python Usage
Here's how to use Whisper in your Python applications:
import whisper
# Load the model
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
# Transcribe audio
result = model.transcribe("audio.mp3")
print(result["text"])Advanced Usage with Language Detection
For more control over the transcription process:
import whisper
# Load model
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
# Load and preprocess audio
audio = whisper.load_audio("audio.mp3")
audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio)
# Create mel spectrogram
mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio, n_mels=model.dims.n_mels).to(model.device)
# Detect language
_, probs = model.detect_language(mel)
detected_language = max(probs, key=probs.get)
print(f"Detected language: {detected_language}")
# Decode audio
options = whisper.DecodingOptions()
result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options)
print(f"Transcription: {result.text}")Real-World Applications
1. Meeting Transcription System
import whisper
import os
from datetime import datetime
def transcribe_meeting(audio_file, output_dir="transcripts"):
"""Transcribe meeting audio and save to file"""
model = whisper.load_model("medium")
# Transcribe with timestamps
result = model.transcribe(audio_file, verbose=True)
# Create output directory
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# Generate filename with timestamp
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
output_file = f"{output_dir}/meeting_{timestamp}.txt"
# Save transcription
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(f"Meeting Transcription - {datetime.now()}\n")
f.write("=" * 50 + "\n\n")
f.write(result["text"])
print(f"Transcription saved to: {output_file}")
return result
# Usage
transcribe_meeting("meeting_recording.mp3")2. Multilingual Content Processing
import whisper
import json
def process_multilingual_content(audio_files):
"""Process multiple audio files in different languages"""
model = whisper.load_model("large")
results = []
for audio_file in audio_files:
print(f"Processing: {audio_file}")
# Transcribe with language detection
result = model.transcribe(audio_file, task="transcribe")
# Also get English translation if not English
translation = None
if result.get("language") != "en":
translation = model.transcribe(audio_file, task="translate")
results.append({
"file": audio_file,
"language": result.get("language"),
"transcription": result["text"],
"translation": translation["text"] if translation else None
})
return results
# Usage
audio_files = ["english.wav", "spanish.wav", "french.wav"]
results = process_multilingual_content(audio_files)
# Save results
with open("multilingual_results.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(results, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)Performance Optimization Tips
1. Choose the Right Model
- For real-time applications: Use tiny or base models
- For high accuracy: Use medium or large models
- For English-only: Use .en models for better performance
- For balanced performance: Use turbo model
2. Optimize Audio Input
import whisper
import librosa
def optimize_audio_for_whisper(audio_file):
"""Optimize audio file for better Whisper performance"""
# Load audio with librosa for preprocessing
audio, sr = librosa.load(audio_file, sr=16000) # Whisper expects 16kHz
# Normalize audio
audio = librosa.util.normalize(audio)
# Remove silence
audio, _ = librosa.effects.trim(audio, top_db=20)
return audio
# Usage
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
optimized_audio = optimize_audio_for_whisper("noisy_audio.wav")
result = model.transcribe(optimized_audio)3. Batch Processing
import whisper
import os
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def batch_transcribe(audio_directory, model_size="turbo", max_workers=4):
"""Batch process multiple audio files"""
model = whisper.load_model(model_size)
audio_files = [f for f in os.listdir(audio_directory)
if f.endswith(('.mp3', '.wav', '.flac', '.m4a'))]
def transcribe_single(audio_file):
file_path = os.path.join(audio_directory, audio_file)
try:
result = model.transcribe(file_path)
return {"file": audio_file, "text": result["text"], "status": "success"}
except Exception as e:
return {"file": audio_file, "error": str(e), "status": "error"}
# Process files in parallel
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) as executor:
results = list(executor.map(transcribe_single, audio_files))
return results
# Usage
results = batch_transcribe("./audio_files", model_size="medium")
for result in results:
if result["status"] == "success":
print(f"{result['file']}: {result['text'][:100]}...")
else:
print(f"Error processing {result['file']}: {result['error']}")Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
- Missing FFmpeg: Install FFmpeg using your system's package manager
- Rust compilation errors: Install Rust development environment
- Memory issues: Use smaller models or process shorter audio segments
Performance Issues
- Slow transcription: Use smaller models or enable GPU acceleration
- Poor accuracy: Try larger models or preprocess audio to remove noise
- Language detection errors: Manually specify the language parameter
Integration with Other Tools
FastAPI Web Service
from fastapi import FastAPI, File, UploadFile
import whisper
import tempfile
import os
app = FastAPI()
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
@app.post("/transcribe/")
async def transcribe_audio(file: UploadFile = File(...)):
"""API endpoint for audio transcription"""
# Save uploaded file temporarily
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix=".wav") as tmp_file:
content = await file.read()
tmp_file.write(content)
tmp_file_path = tmp_file.name
try:
# Transcribe audio
result = model.transcribe(tmp_file_path)
return {
"transcription": result["text"],
"language": result.get("language", "unknown")
}
finally:
# Clean up temporary file
os.unlink(tmp_file_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)Conclusion
OpenAI Whisper represents a significant advancement in speech recognition technology. Its multilingual capabilities, ease of use, and robust performance make it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, from simple transcription tasks to complex multilingual processing systems.
Key takeaways:
- Choose the right model size based on your speed vs. accuracy requirements
- Preprocess audio for optimal results
- Use English-only models when possible for better performance
- Consider batch processing for large-scale applications
- Implement proper error handling and fallback mechanisms
With over 88,000 stars on GitHub and active development, Whisper continues to evolve and improve. Whether you're building a meeting transcription service, a multilingual content platform, or integrating speech recognition into your AI applications, Whisper provides the robust foundation you need.
For more expert insights and tutorials on AI and automation, visit us at decisioncrafters.com.